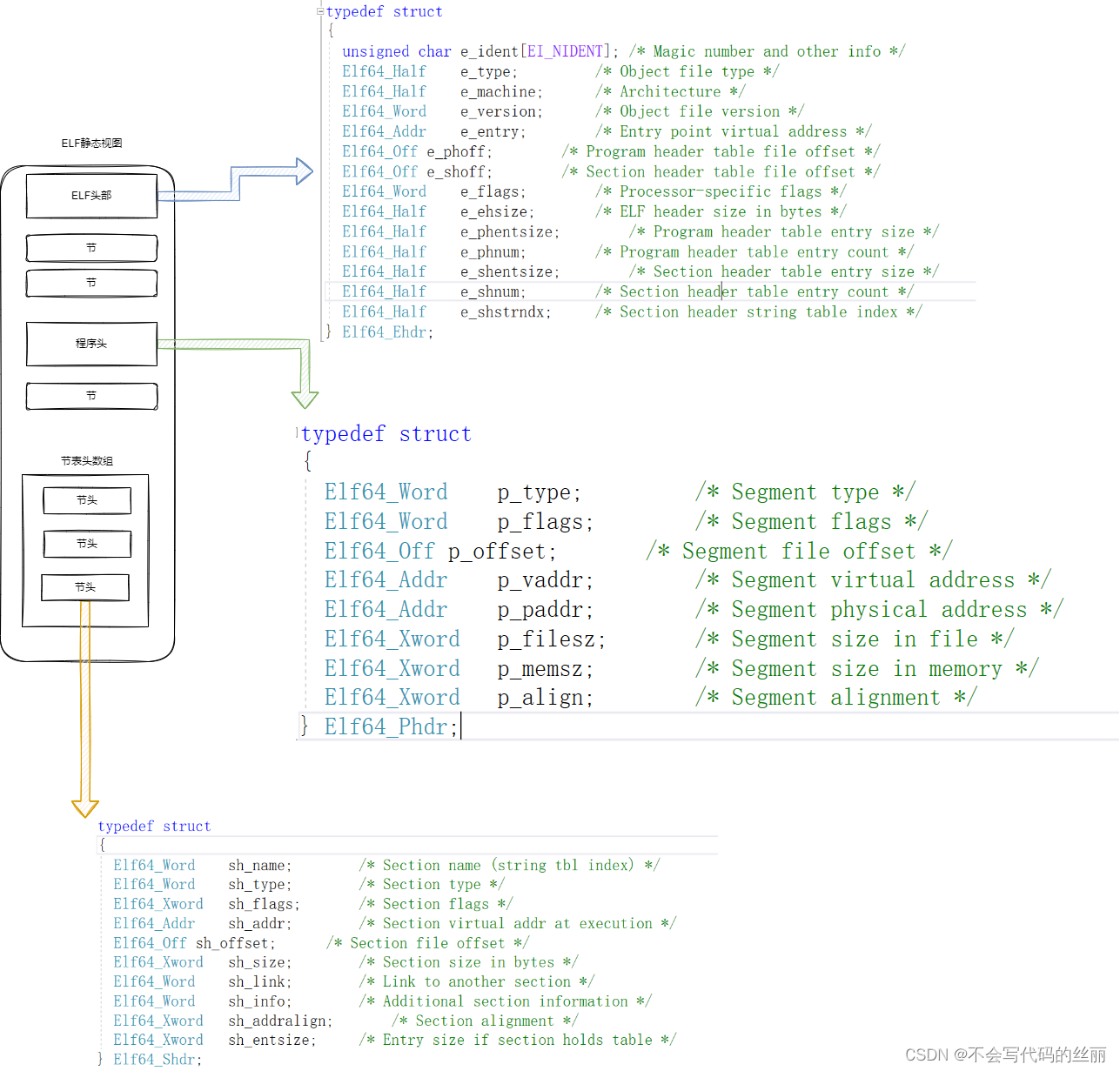
一、基础 ELF文件 整体架构 elf文件主要分了几部分:头部、程序头、节表头以及各种节.
elf头部中存储了程序头和节表头的位置,节头中又存储了各个节的位置,以此进行索引.
所以可以回答第2个问题的一部分, 这些节(我认为题目应该说的是节的意思, 段和节经常混用) 在ELF中的位置是可以任意调换的,因为在头部中指定了它们的位置,只要索引信息没问题就可以.
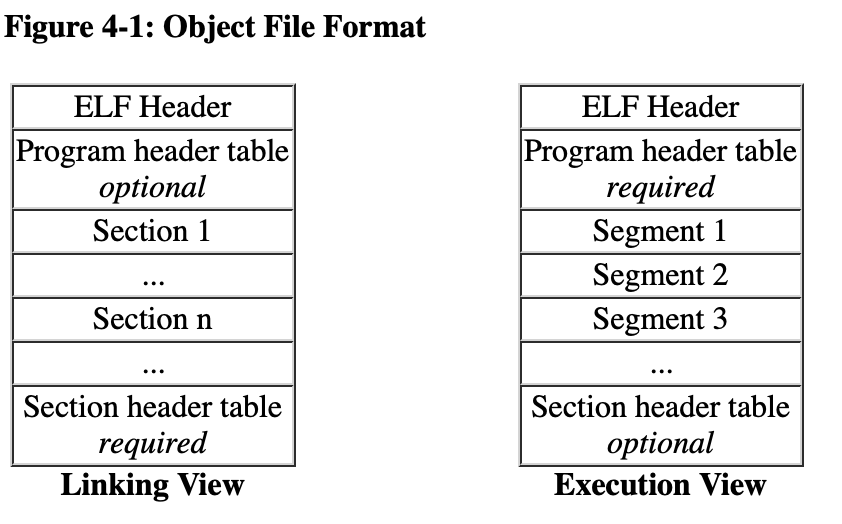
链接视图与执行时视图 elf静态文件是链接视图,当加载到内存后,会有些许变化.
在链接视图中,节表是必须的,需要根据它来定位各个节,以及保存节的属性,而程序头表则是可选的,程序头表的内容是加载进内存后的属性(是否可选要看该文件的类型?? ).
在执行视图中,程序头表是必须的,节表就是可选的了.
在静态文件中,有各种不一样的程序的节(section),比如.text节 .bss节,在加载进内存后,加载器会将相同的节属性(比如只读)合并一个段(segment)
ELF文件头 ehdr 详细内容:https://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/elf/gabi4+/ch4.eheader.html
结构体定义如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #define EI_NIDENT 16 typedef struct { unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; Elf32_Half e_type; Elf32_Half e_machine; Elf32_Word e_version; Elf32_Addr e_entry; Elf32_Off e_phoff; Elf32_Off e_shoff; Elf32_Word e_flags; Elf32_Half e_ehsize; Elf32_Half e_phentsize; Elf32_Half e_phnum; Elf32_Half e_shentsize; Elf32_Half e_shnum; Elf32_Half e_shstrndx; } Elf32_Ehdr; typedef struct { unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */ Elf64_Half e_type; /* Object file type */ elf文件类型 Elf64_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */ CPU架构 Elf64_Word e_version; /* Object file version */ 指定ELF版本,一般都为1 Elf64_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */ 代码运行的入口 Elf64_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */ 程序头表在文件中的偏移 Elf64_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */ 节头表在文件中的偏移 Elf64_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */ 在e_machine指定的处理器下的一些特性 Elf64_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */ Elf64_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */ 程序头表每个条目的大小 Elf64_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */ 程序头表中条目的树木 Elf64_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */ 节头表每个条目的大小 Elf64_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */ 节头表中条目的数量 Elf64_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */ 每个节都有一个名称,这些名称存储在.shstrtab节中,e_shstrndx指定这个特殊的节所在节头表的下表 } Elf64_Ehdr;
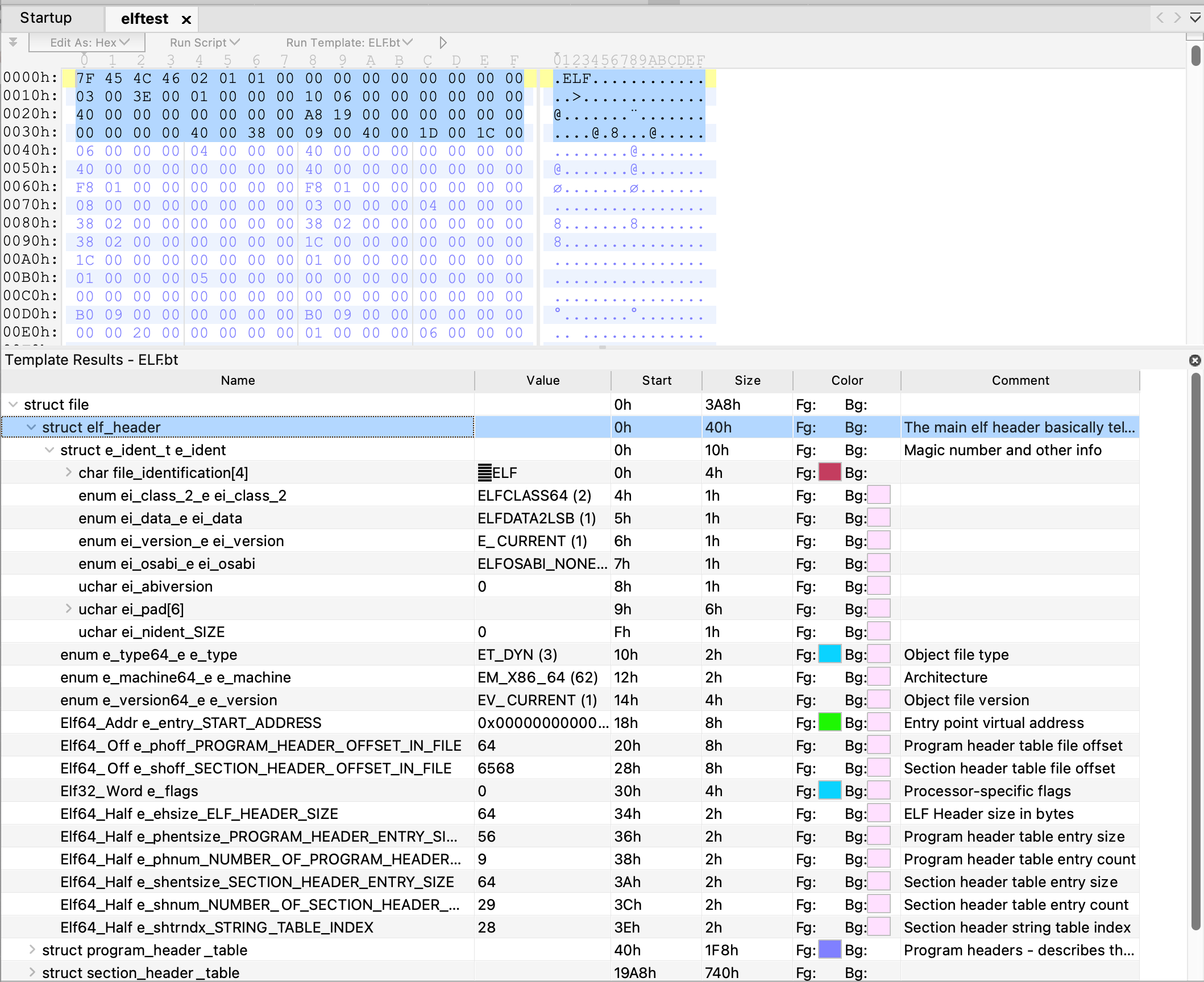
可以用010editor加载插件后清晰的看到结构(需要在templates里面安装和加载一下elf模版)
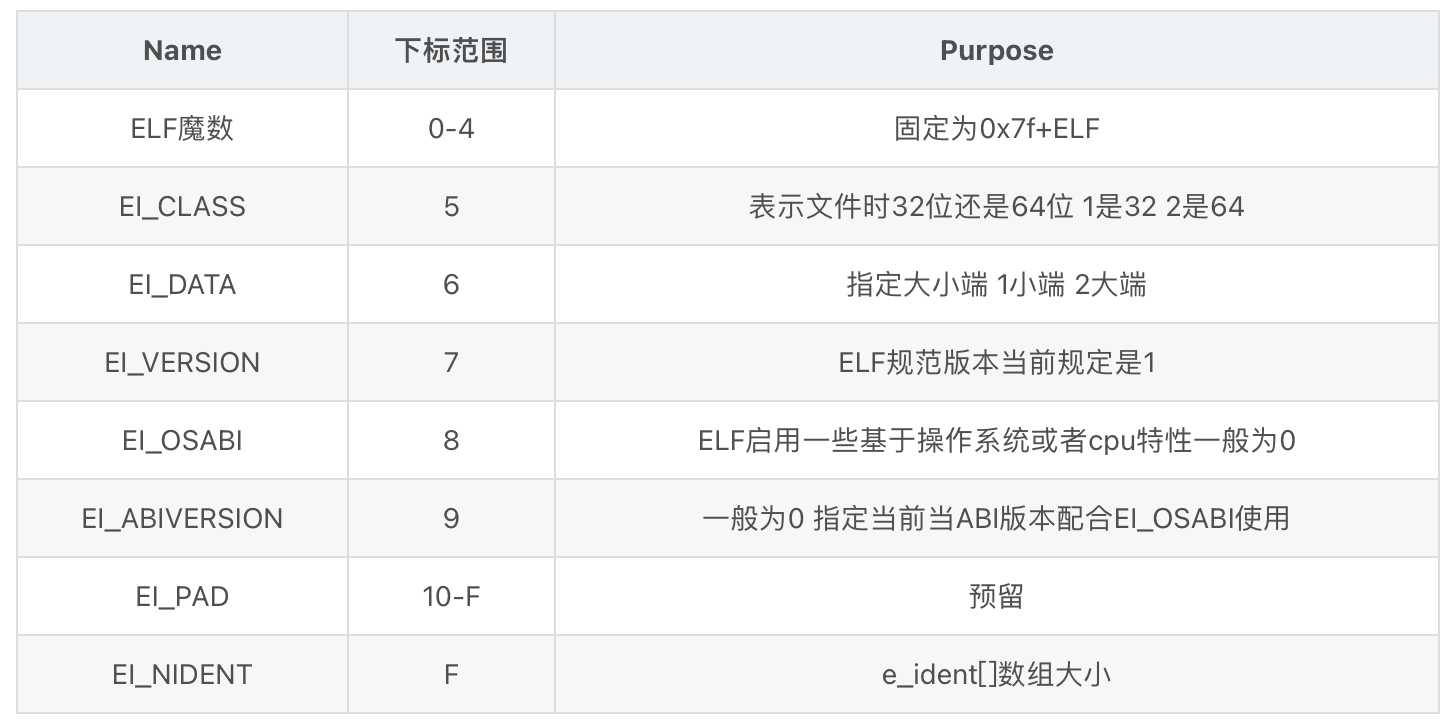
e_ident 一个16字节大小的数组
这个下标范围标错了吧….
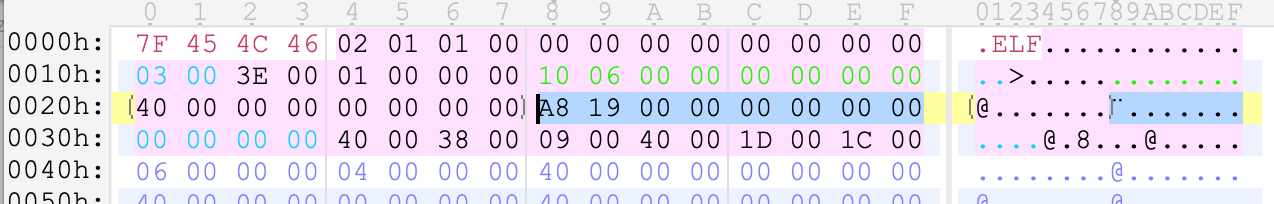
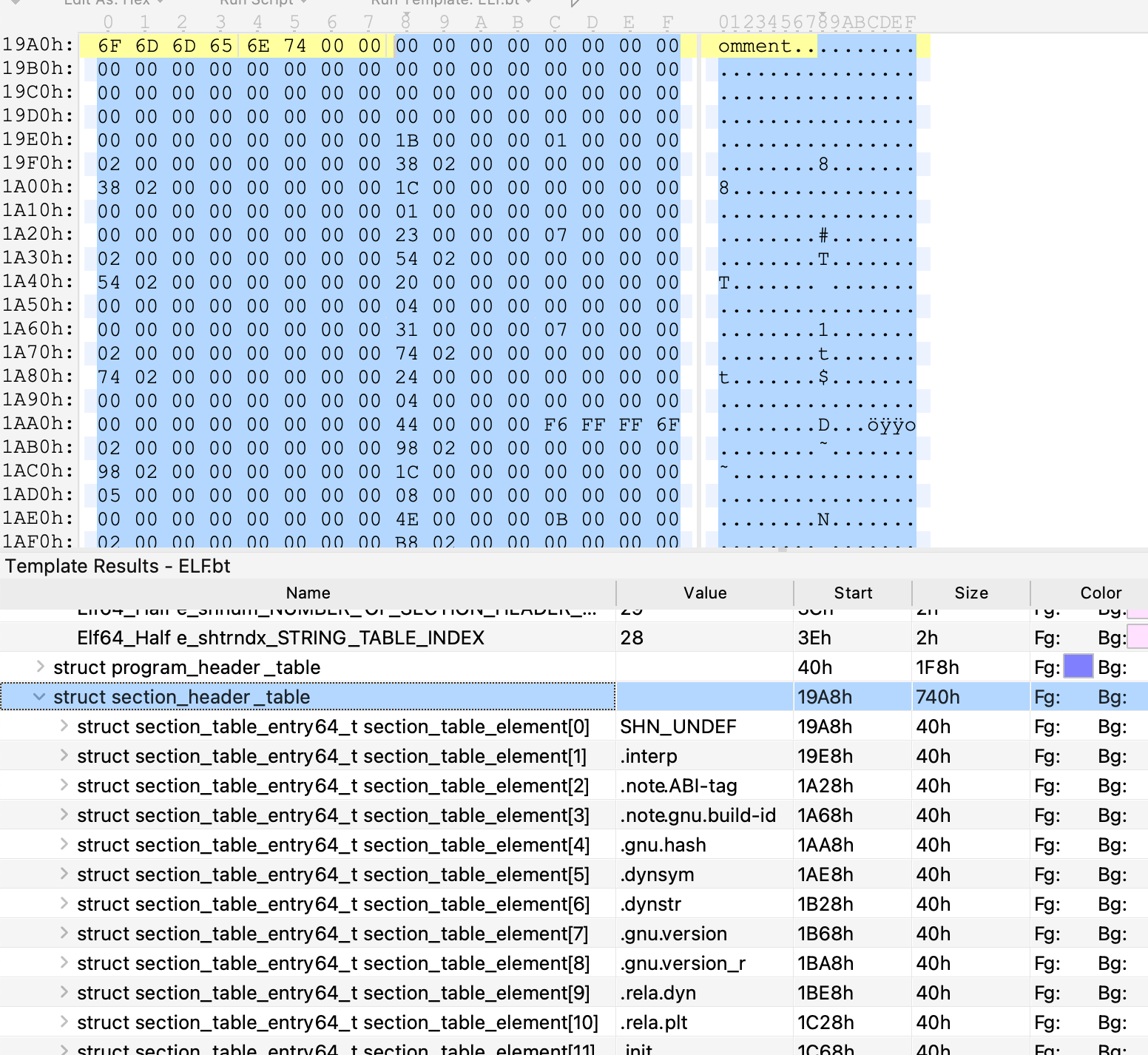
ELF节表头 shdr e_shoff是 0x19a8(小端)
可以看到0x19a8开始,存储的是各个节的内容
结构如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 /* Section header. */ typedef struct { Elf32_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */ Elf32_Word sh_type; /* Section type */ Elf32_Word sh_flags; /* Section flags */ Elf32_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */ Elf32_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */ Elf32_Word sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */ Elf32_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */ Elf32_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */ Elf32_Word sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */ Elf32_Word sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */ } Elf32_Shdr; typedef struct { Elf64_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */ 名称,值是在string表的索引 Elf64_Word sh_type; /* Section type */ Elf64_Xword sh_flags; /* Section flags */ 标记属性 读写执行 Elf64_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */ 虚拟地址 Elf64_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */ 在文件中的偏移 Elf64_Xword sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */ 大小 Elf64_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */ Elf64_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */ Elf64_Xword sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */ Elf64_Xword sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */ } Elf64_Shdr;
sh_name 这里存储的是节名的下标,节名实际存在于.shstrtab中,这里存的是在shstrtab中的下标.
节 section .text节 保存了程序代码指令的代码节. 一段可执行程序如果存在Phdr, .text字节就会存在于text段中(如果不存在呢?? )
.rodata节 保存只读数据,如一行c语言代码中的字符串 printf(“hello world\n”); 因为是只读,所以也放到了text段
.data节 保存了初始的全局变量等数据.存在于data段
.bss节 保存了未进行初始化的全局数据,存在于data段.
.plt 包含了动态链接器调用从共享库导入的函数所必需的相关代码. 存在于text段中,同样保存了代码.
.got 保存了全局偏移表.这个存的是变量
.got.plt 这个存的是函数引用
.dynsym 保存了从共享库导入的动态符号信息,该节保存在text段中
.dynstr 保存了动态符号字符串表,表中存放了一系列字符串,这些字符串表示符号的名称,以空字符00作为终止符
ELF程序头 phdr (segment段) 程序头中描述了可执行文件的段信息,即程序如何加载到内存以及内存中的布局.
程序头可以通过elf文件头的e_phoff(程序头表偏移量)字段来得到位置
它主要有5种类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 typedef struct { Elf32_Word p_type; Elf32_Off p_offset; Elf32_Addr p_vaddr; Elf32_Addr p_paddr; Elf32_Word p_filesz; Elf32_Word p_memsz; Elf32_Word p_flags; Elf32_Word p_align; } Elf32_Phdr; typedef struct { Elf64_Word p_type; Elf64_Word p_flags; Elf64_Off p_offset; Elf64_Addr p_vaddr; Elf64_Addr p_paddr; Elf64_Xword p_filesz; Elf64_Xword p_memsz; Elf64_Xword p_align; } Elf64_Phdr;
PT_LOAD 一个可执行文件至少有一个该类型的段.PT_LOAD表述的是可装载的段,这种类型的段会被装载或者映射到内存中,
编译器如何对节段进行组织安排 这里所说的是编译环节,从源代码到二进制文件.
ELF装载过程 这里是指把二进制文件加载进内存的过程
问题 一个elf程序或者动态库是否必须有某些节,他们固定的名字和含义
编译器如何对这些段进行编排和组织,顺序是否可以任意调换
是否可以欺骗程序加载器或者反汇编引擎(例如,增、删、改text段)
文件头52????
magic number16字节 还剩36字节
8*2 + 4 * 2 + 4 + 4 * 2 = 36
0x3e = 62
测试 删除一些段,程序是否还能正常运行? 程序必须的段 节是哪些??
怎么增删改text段等 欺骗编译器等
代码编写 自己也要编译成32位才行
gcc -m32 1.c && ./a.out test
可以参考readelf
先把32位的都给写好,然后再加上64位的
1.改进,32位 64位,根据文件头判断,然后再进行解析
解析段和节,名称 起始和结束位置, 大小,权限
fatal error: elf32.h: No such file or directory
fatal error: bits/libc-header-start.h: No such file or directory
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54082459/fatal-error-bits-libc-header-start-h-no-such-file-or-directory-while-compili
e_ident 怎么输出多位, c
怎么定义空格字符呢?
gcc -m32 1.c 需要编译成32位的,目前也只能解析32位程序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <elf.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/mman.h> #include <stdint.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main (int argc, char **argv) { int fd, i; uint8_t *mem; struct stat st ; char *StringTable, *interp; Elf32_Ehdr *Elf_header; Elf32_Phdr *Pro_header; Elf32_Shdr *Section_header; if (argc < 2 ) { printf ("usage: %s <executable> \n" , argv[0 ]); exit (0 ); } if ((fd = open(argv[0 ], O_RDONLY)) < 0 ) { perror("open" ); exit (-1 ); } if (fstat(fd, &st) < 0 ) { perror("fstat" ); exit (-1 ); } mem = mmap(NULL , st.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, fd, 0 ); if (mem[4 ] == 0x2 ) printf ("it is 64 bit %d\n" ,mem[4 ]); else printf ("it is 32 bit %d\n" ,mem[4 ]); Elf_header = (Elf32_Ehdr *)mem; printf ("\n" ); printf ("e_ident: \t%10x\n" ,Elf_header->e_ident[16 ]); printf ("Type: \t%d\n" ,Elf_header->e_type); printf ("Machine: \t%d\n" ,Elf_header->e_machine); printf ("Version: \t%#02x\n" ,Elf_header->e_version); printf ("Entry point address: \t%#02x\n" ,Elf_header->e_entry); printf ("Start of program headers: \t%d(bytes)\n" ,Elf_header->e_phoff); printf ("Start of section headers: \t%d(bytes)\n" ,Elf_header->e_shoff); printf ("Flags: \t%#02x\n" ,Elf_header->e_flags); printf ("Size of this header: \t%d(bytes)\n" ,Elf_header->e_ehsize); printf ("Size of program headers: \t%d(bytes)\n" ,Elf_header->e_phentsize); printf ("Number of program headers: \t%d\n" ,Elf_header->e_phnum); printf ("Size of section headers: \t%d(bytes)\n" ,Elf_header->e_shentsize); printf ("Number of section headers: \t%d\n" ,Elf_header->e_shnum); printf ("Section header string table index:\t%d\n" ,Elf_header->e_shstrndx); Section_header = (Elf32_Shdr *)&mem[Elf_header->e_shoff]; StringTable = &mem[Section_header[Elf_header->e_shstrndx].sh_offset]; printf ("Section header list:\n\n" ); char a = '|' ; printf ("[Nr] Name%-20c\t\tType%-10c\tAddr\t\tOff\tSize\tES Flg Al" ,a); for (i = 1 ; i<Elf_header->e_shnum; i++) { printf ("\n[%-2d] %-20s\t\t%-10x\t%08x\t%06x\t%06x\t%02x %02x %02x " \ , i,&StringTable[Section_header->sh_name],Section_header->sh_type,Section_header->sh_addr,\ Section_header->sh_offset,Section_header->sh_size,Section_header->sh_entsize,\ Section_header->sh_flags,Section_header->sh_addralign); Section_header++; } Pro_header = (Elf32_Phdr *)&mem[Elf_header->e_phoff]; printf ("\n" ); printf ("\n/*****Program Headers:*****/\n" ); printf ("starting at offset: %d\n" ,Elf_header->e_phoff); printf ("Number of program headers: %d\n" ,Elf_header->e_phnum); printf ("Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr FileSiz MemSiz Flg\n" ); for (i = 0 ; i<Elf_header->e_phnum; i++) { printf ("%d %-#6x %-#x %-#x %-#5x %-#5x %-#x\n" ,Pro_header->p_type,Pro_header->p_offset,\ Pro_header->p_vaddr,Pro_header->p_paddr\ ,Pro_header->p_filesz,Pro_header->p_memsz,Pro_header->p_flags); Pro_header++; } return 0 ; }
参考 ELF(5)手册
ELF官方规范文档
https://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/elf/gabi4+/contents.html
https://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/elf/gabi4+/ch4.eheader.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qfanmingyiq/article/details/124295287
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/401446080?utm_id=0
https://github.com/jianhong-li/ElfReader
https://www.52pojie.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=591986&highlight=elf%2B%BD%E2%CE%F6