第六章 结构
结构还是很重要的,在编写大型程序的时候,或者平常看源代码,会看到非常多的结构体
6.1 结构的基本知识
在写这个程序的时候遇到了很奇怪的问题,dist = sqrt(4.0);不会报错,但是dist = sqrt(a);就会报错,百思不得其解.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void main()
{
struct point {
int x;
int y;
};
struct point maxpt = {320,200};
printf("length: %d, width: %d\n",maxpt.x,maxpt.y);
double dist;
printf("%f\n",(double)maxpt.x * maxpt.x + (double)maxpt.y * maxpt.y);
dist = sqrt(4.0);
double test = (double)maxpt.x * maxpt.x + (double)maxpt.y * maxpt.y;
double a = 4.0;
dist = sqrt(a);
printf("duijiaoxian: %f\n",dist);
}
|
神奇的gpt,所以是编译优化的事, 优化过后不用这个函数了,所以好像是显得没有问题一样,可以用gdb调试,会发现这里根本没有调用函数

1
2
3
| ► 0x5555555551b5 <main+108> movsd xmm0, qword ptr [rip + 0xe7b]
0x5555555551bd <main+116> movsd qword ptr [rbp - 0x20], xmm0
0x5555555551c2 <main+121> mov eax, dword ptr [rbp - 8]
|
链接上就好了 gcc main.c -lm
1
2
| ► 0x555555555244 <main+219> call sqrt@plt <sqrt@plt>
x: 0x7ffff7e5f7e0 (_IO_stdfile_1_lock) ◂— 0x0
|
6.2 结构与函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
struct point {
int x;
int y;
};
struct rect {
struct point pt1;
struct point pt2;
};
struct point makepoint(int x,int y)
{
struct point temp;
temp.x = x;
temp.y = y;
return temp;
};
void main()
{
struct rect screen;
struct point middle;
struct point makepoint(int,int);
int XMAX, YMAX;
XMAX = YMAX = 0;
screen.pt1 = makepoint(100,100);
screen.pt2 = makepoint(XMAX,YMAX);
middle = makepoint((screen.pt1.x + screen.pt2.x)/2, (screen.pt1.y+screen.pt2.y)/2);
printf("middle's x= %d, middle's y = %d\n",middle.x,middle.y);
}
|
6.3 结构数组
需要注意各种定义的先后顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXWORD 100
struct key{
char *word;
int count;
} keytab[] = {
"auto",0,
"break",0,
"case",0,
"char",0,
"const",0,
"continue",0,
"default",0,
"unsigned",0,
"void",0,
"volatile",0,
"while",0
};
#define NKEYS (sizeof keytab / sizeof keytab[0])
int getword(char *,int);
int binsearch(char *, struct key *,int);
int main()
{
int n;
char word[MAXWORD];
while (getword(word,MAXWORD) != EOF)
if (isalpha(word[0]))
if((n = binsearch(word, keytab, NKEYS)) >= 0)
keytab[n].count++;
printf("test\n");
printf("%d\n",NKEYS);
for(n=0; n < NKEYS;n++)
if(keytab[n].count >0)
printf("%4d %s\n",keytab[n].count, keytab[n].word);
return 0;
}
int binsearch(char *word,struct key tab[],int n)
{
int cond;
int low,high,mid;
low = 0;
high = n-1;
while(low <= high)
{
mid = (low + high)/2;
if ((cond = strcmp(word,tab[mid].word)) < 0)
high = mid - 1;
else if(cond > 0)
low = mid + 1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}
int getword(char *word, int lim)
{
int c,getch(void);
void ungetch(int);
char *w = word;
while (isspace(c = getch())) ;
if (c!=EOF)
*w++ = c;
if(!isalpha(c)){
*w = '\0';
return c;
}
for(; --lim >0; w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
*w = '\0';
return word[0];
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp = 0;
int getch(void)
{
return (bufp > 0)? buf[--bufp] : getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c)
{
if (bufp >= BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++] = c;
}
|
<ctype.h>中
isspace 判断是否是空白符号, isalpha判断是否是字母,isalnum判断是否是数字或字母
标准的空白字符
1
2
3
4
5
6
| ' ' (0x20) space (SPC) 空格符
'\t' (0x09) horizontal tab (TAB) 水平制表符
'\n' (0x0a) newline (LF) 换行符
'\v' (0x0b) vertical tab (VT) 垂直制表符
'\f' (0x0c) feed (FF) 换页符
'\r' (0x0d) carriage return (CR) 回车符
|
ctrl+d获取EOF结束输入
6.4 指向结构的指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXWORD 100
struct key{
char *word;
int count;
} keytab[] = {
"auto",0,
"break",0,
"case",0,
"char",0,
"const",0,
"continue",0,
"default",0,
"unsigned",0,
"void",0,
"volatile",0,
"while",0
};
#define NKEYS (sizeof keytab / sizeof keytab[0])
int getword(char *,int);
struct key *binsearch(char *, struct key *,int);
int main()
{
char word[MAXWORD];
struct key *p;
while (getword(word,MAXWORD) != EOF)
if (isalpha(word[0]))
if((p = binsearch(word, keytab, NKEYS)) != NULL)
p->count++;
for(p = keytab; p < keytab + NKEYS;p++)
if(p->count >0)
printf("%4d %s\n",p->count, p->word);
return 0;
}
struct key *
binsearch(char *word,struct key *tab,int n)
{
int cond;
struct key *low = &tab[0];
struct key *high = &tab[n];
struct key *mid;
while(low < high)
{
mid = low + (high-low)/2;
if ((cond = strcmp(word,mid->word)) < 0)
high = mid;
else if(cond > 0)
low = mid + 1;
else
return mid;
}
return NULL;
}
int getword(char *word, int lim)
{
int c,getch(void);
void ungetch(int);
char *w = word;
while (isspace(c = getch())) ;
if (c!=EOF)
*w++ = c;
if(!isalpha(c)){
*w = '\0';
return c;
}
for(; --lim >0; w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
*w = '\0';
return word[0];
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp = 0;
int getch(void)
{
return (bufp > 0)? buf[--bufp] : getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c)
{
if (bufp >= BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++] = c;
}
|
6.5 自引用结构
用二叉树来存储
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXWORD 100
struct tnode *addtree(struct tnode *p, char *w);
void treeprint(struct tnode *p);
struct tnode *talloc(void);
char *strdup1(char *s);
int getword(char *word, int lim);
struct tnode{
char *word;
int count;
struct tnode *left;
struct tnode *right;
};
int main()
{
struct tnode *root;
char word[MAXWORD];
root = NULL;
while(getword(word,MAXWORD)!=EOF)
if(isalpha(word[0]))
root = addtree(root,word);
treeprint(root);
return 0;
}
struct tnode *talloc(void);
struct tnode *addtree(struct tnode *p, char *w)
{
int cond;
if (p == NULL)
{
p = talloc();
p->word = strdup1(w);
p->count = 1;
p->left = p->right = NULL;
}else if ((cond = strcmp(w,p->word)) == 0 )
p->count++;
else if(cond < 0)
p->left = addtree(p->left,w);
else
p->right=addtree(p->right,w);
return p;
}
void treeprint(struct tnode *p)
{
if (p!=NULL)
{
treeprint(p->left);
printf("%4d %s\n",p->count,p->word);
treeprint(p->right);
}
}
#include <stdlib.h>
struct tnode *talloc(void)
{
return (struct tnode *) malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
}
char *strdup1(char *s)
{
char *p;
p = (char *) malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if (p != NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
int getword(char *word, int lim)
{
int c,getch(void);
void ungetch(int);
char *w = word;
while (isspace(c = getch())) ;
if (c!=EOF)
*w++ = c;
if(!isalpha(c)){
*w = '\0';
return c;
}
for(; --lim >0; w++)
if(!isalnum(*w=getch())){
ungetch(*w);
break;
}
*w = '\0';
return word[0];
}
#define BUFSIZE 100
char buf[BUFSIZE];
int bufp = 0;
int getch(void)
{
return (bufp > 0)? buf[--bufp] : getchar();
}
void ungetch(int c)
{
if (bufp >= BUFSIZE)
printf("ungetch: too many characters\n");
else
buf[bufp++] = c;
}
|
6.6 表查找
之前学过的,用散列等方法,进行查表
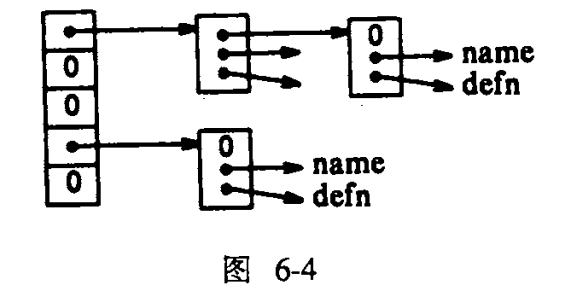
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| struct nlist{
struct nlist *next;
char *name;
char *defn;
};
#define HASHSIZE 101
static struct nlist *hashtab[HASHSIZE];
|
散列函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
unsigned hash(char *s)
{
unsigned hashval;
for(hashval=0; *s !='\0';s++)
hashval = *s + 31* hashval;
return hashval % HASHSIZE:
}
|
查找函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| struct nlist *lookup(char *s)
{
struct nlist *np;
for (np = hashtab[hash(s)]; np != NULL; np = np->next)
if (strcmp(s, np->name) == 0)
return np;
return NULL;
}
|
加入函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| struct nlist *lookup(char *s);
char *strdup(char *);
struct nlist *install(char *name, char *defn)
{
struct nlist *np;
unsigned hashval;
if((np = lookup(name)) == NULL){
np = (struct nlist *) malloc(sizeof(*np));
if (np == NULL || (np->name = strdup(name)) == NULL)
return NULL;
hashval = hash(name);
np->next = hashtab[hashval];
hashtab[hashval] = np;
}else
free((void *)np->defn)
if((np->defn = strdup(defn)) == NULL)
return NULL
return np;
}
|
整合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct nlist{
struct nlist *next;
char *name;
char *defn;
};
#define HASHSIZE 101
static struct nlist *hashtab[HASHSIZE];
struct nlist *lookup(char *s);
char *strdup1(char *);
unsigned hash(char *s);
struct nlist *install(char *name, char *defn);
int main()
{
printf("1.add\n");
char *name,*defn;
name = (char *)malloc(100);
defn = (char *)malloc(100);
if (name == NULL || defn == NULL){
printf("内存分配失败\n");
return 1;
}
while(1){
printf("请输入名字和替换的名字");
scanf("%s %s",name,defn);
install(name,defn);
}
free(name);
free(defn);
return 0;
}
unsigned hash(char *s)
{
unsigned hashval;
for(hashval=0; *s !='\0';s++)
hashval = *s + 31* hashval;
return hashval % HASHSIZE;
}
struct nlist *lookup(char *s)
{
struct nlist *np;
for (np = hashtab[hash(s)]; np != NULL; np = np->next)
if (strcmp(s, np->name) == 0)
return np;
return NULL;
}
struct nlist *install(char *name, char *defn)
{
struct nlist *np;
unsigned hashval;
if((np = lookup(name)) == NULL){
np = (struct nlist *) malloc(sizeof(*np));
if (np == NULL || (np->name = strdup(name)) == NULL)
return NULL;
hashval = hash(name);
np->next = hashtab[hashval];
hashtab[hashval] = np;
}else
free((void *) np->defn);
if((np->defn = strdup1(defn)) == NULL)
return NULL;
return np;
}
char *strdup1(char *s)
{
char *p;
p = (char *) malloc(strlen(s)+1);
if (p != NULL)
strcpy(p,s);
return p;
}
|
6.7 6.8 类型定义(typedef)、位字段
第七章 输入与输出
7.1 标准输入输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
int c;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
putchar(tolower(c));
return 0;
}
|
7.2 格式化输出 printf函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| #include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char *s = "hello,lihua";
printf(s);
printf("\n");
printf("%s\n",s);
}
|
7.3 变长参数表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| #include <stdarg.h>
void minprintf(char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
char *p, *sval;
int ival;
double dval;
va_start(ap, fmt);
for (p= fmt; *p; p++)
{
if( *p!='%'){
putchar(*p);
continue;
}
switch(*++p){
case 'd':
ival = va_arg(ap,int);
printf("%d", ival);
break;
case 'f':
dval = va_arg(ap, double);
printf("%f",dval);
break;
case 's':
for (sval = va_arg(ap, char *); *sval; sval++)
putchar(*sval);
break;
default:
putchar(*p);
break;
}
}
va_end(ap);
}
int main()
{
minprintf("hello,wolrd:%d,%s\n",1,"ooo");
}
|
7.4 格式化输入 scanf函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| #include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double sum, v;
sum = 0 ;
while( scanf("%lf", &v) == 1)
printf("\t%.2f\n",sum+=v);
return 0;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| #include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int day,month,year;
scanf("%d/%d/%d",&month,&day,&year);
printf("%d年%d月%d日\n",year,month,day);
return 0;
}
|
7.5 文件访问
这里和pwn的iofile关系很大
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| #include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
void filecopy(FILE *, FILE *);
if (argc == 1) filecopy(stdin,stdout);
else
while(--argc > 0)
if((fp = fopen(*++argv,"r")) == NULL){
printf("cat: can't open %s\n",*argv);
return 1;
}else{
filecopy(fp,stdout);
fclose(fp);
}
return 0;
}
void filecopy(FILE *ifp,FILE *ofp)
{
int c;
while( (c = getc(ifp))!=EOF)
putc(c,ofp);
}
|
gdb调试一下 , 可以结合之前看的open什么的那个链来学习一下
7.6 错误处理
增加了stderr
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp;
void filecopy(FILE *, FILE *);
char *prog = argv[0];
if (argc == 1) filecopy(stdin,stdout);
else
while(--argc > 0)
if((fp = fopen(*++argv,"r")) == NULL){
fprintf(stderr," %s: can't open %s\n",prog,*argv);
exit(1);
}else{
filecopy(fp,stdout);
fclose(fp);
}
if (ferror(stdout))
{
fprintf(stderr,"%s: error writing stdout\n", prog);
exit(2);
}
exit(0);
}
void filecopy(FILE *ifp,FILE *ofp)
{
int c;
while( (c = getc(ifp))!=EOF)
putc(c,ofp);
}
|
7.7 行输入和行输出
7.8 特别有用的函数(更详细的在附录b中)
EOF与空白符号的区别
这是空白符号, EOF是-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
| ' ' (0x20) space (SPC) 空格符
'\t' (0x09) horizontal tab (TAB) 水平制表符
'\n' (0x0a) newline (LF) 换行符
'\v' (0x0b) vertical tab (VT) 垂直制表符
'\f' (0x0c) feed (FF) 换页符
'\r' (0x0d) carriage return (CR) 回车符
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fp;
int c;
fp = fopen("./flag","r");
while(1)
{
c = fgetc(fp);
if(feof(fp)) break;
printf("%c",c);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
|